Somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT)・ Oocytes Nuclear Transfer
APPLICATIONS
Generation of cloned calves and transgenic chimeric embryos from bovine embryonic stem-like cells
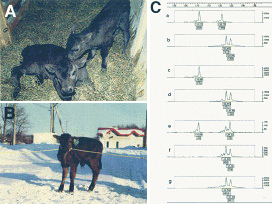
Fig. 1. Photographs of calves obtained after nuclear transfer.
A: Two days after birth
B: Four weeks after birth
C: Fingerprinting of DNA from cloned calves, recipient cows, and donor ES-like W3 cells. Electrophoretograms show amplified fragments of DNA derived from leukocytes from recipient cows (panels a, c and e) and cloned calves (panels b, d and f) and from donor ES-like W3 cells (panel g).
Upper and right-side scales indicate the sizes of DNAs (bp) and the intensities of DNA fragments, respectively. Numbers in boxes indicate the sizes of DNAs (upper) and the intensities of DNA fragments (lower). After insertion of donor ES-like cells into the perivitelline space of oocytes, cells and cytoplasts were fused electrically in fusion medium.
(DC: 20V, Pulse length: 50us, Pulse interval: 100ms, 2 Pulses)
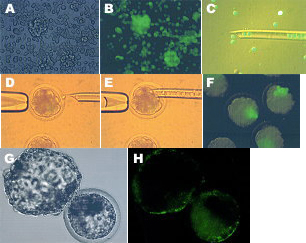
Fig. 2.Expression of EGFP in transgenic chimeric embryos derived from ES-like cells.
A: Phase-contrast image of EGFPtransgenic ES-like cells. Magnification: 200x
B: Fluorescence microscopy image of (A)
C: Ten to fifteen ES-like cells being injected into embryos at 8- to 16-cell stage.
(Fluorescence phase-contrast image)
D, E: Micromanipulation procedures for the formation of chimeric embryos generated by EGFP transgenic ES-like cells and recipient embryos by in vitro fertilization. Magnification: 200x
F: Proliferation of transfected ES-like cells after one day in culture following the formation of chimeric embryos. Magnification: 200x
G: EGFP transgenic blastcysts four days after injection of G418-selected ES-like W3 cells that had been transfected with pCX-Neo-EGFP.
H: Fluorescence microscopy image of (G)
Distinct expression of EGFP was apparent in both the ICM and trophectodermal cells.
Dr. Shigeo Saito, Saito Laboratory of Cell Technology
※Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications,
Volume 309, Issue 1, Pages 104-113, 12 September 2003
PUBLICATIONS
Electroporation
■ Cell Cultures
- Primary Cell Cultures
- Stem Cells
- Organoids
- Cell Lines
- Cells in Adherence
■ In Vivo Mice/Rats
- Zygotes In Vitro (TAKE method)
- Zygotes In Oviduct (i-GONAD method)
- Embryos In Utero
- Ex Utero Embryos In Vitro
- Brain
- Retina / Cornea / Spinal Cord / Sciatic Nerve
- Lung / Spleen / Liver / Stomach/ Kidney / Intestine
- Pancreas / Islets of langerhans
- Testis / Ovary / Prostate / Gonad / Uterus
- Muscle / Skin / Joint / Cartilage / Tumor / Others
■ In Vivo Other Animals
- Bovine/Porcine/Other Animal Zygotes
- Hamster Zygotes in Oviduct (i-GONAD method)
- Monkey Skin
- Chicken (In Ovo・Others)
- Zebrafish & Other Fishes
- Insects・Others
■ Plant Cells & Algae
- Plant Cells
- Algae
■ Exosomes
- Exosomes
■ Bacteria, Yeast, Fungi
- E. coli/Bacterial Cells
- Yeasts/Fungi
- Bacterial cells/Yeasts/Fungi (NEPA Porator)
Drug Delivery and Transfection
■ Ultrasound Transfection and Drug Delivery (Sonoporation/Fus)
- Brain
- Liver/Skin/Other Applications
- Heart
- Cell Culture
- Lung
- Muscle
Electro Cell Fusion
■ Hybridoma Production
- Monoclonal antibodies, etc
■ Oocyte Activation
- Electrical stimulation before/after Intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI)
■ Somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT)・ Oocytes Nuclear Transfer
- Animal cloning
■ Tetraploid Embryos Production
- 2 Cell Embryos (Tetraploid)
■ Other Applications
- Liposome・Protoplast・Yeast, etc.
Fluorescence Quenching / in situ Hybridization Chain Reaction
■ Autofluorescence Quenching
- Mammalian Tissue Sections
- Fish Tissue Sections
- Amphibia Tissue Sections
- Avian Tissue Sections
- Plant Tissue Sections
- Chordate Tissue Sections
■ in situ HCR
- Detection of Target mRNA
Single-Cell/Micro-Particle Transfer
■ マイクロピック&プレースシステム
- Picking and placing micro targets
■ Micro targets
- Animal cells
■ Micro liquid
- Plant cells
Cell Freezing
■ Cell Therapy
- Stem cells, primary cells, and more
■ Animal Husbandry
- Sperm, embryos, tissues, and more