Transfection into Mouse/Rat Brain by Electroporation
APPLICATIONS
Electroporation-mediated gene transfer in the adult rat brain
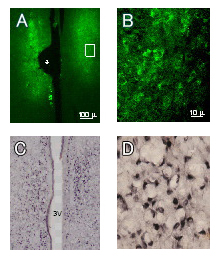
Figure A: EGFP expression in the medial preoptic nuclei of a female rat examined 4 days after bilateral electroporation at 10 weeks of age. (An asterisk indicates the trace of the positioning of the electrode)
Figure B: EGFP-positive cells (high magnification of Fig. A using a 60x objective lens). EGFP fluorescent signals are observed in the perikarya.
Figure C: Estrogen receptor αimmunoreactivity in the medial preoptic nuclei and the periventricular nuclei of an adult female rat.3V: third ventricle.
Figure D: Estrogen receptor α-positive cells (high magnification of Fig. C using a 60x objective lens). Estrogen receptor immunoreactivity is prominent in the nuclei.
Tetsuo Shirakawa, Center for Advanced Oral Medicine, Hokkaido University Hospital
Electroporation-mediated gene transfer system applied to cultured CNS neurons
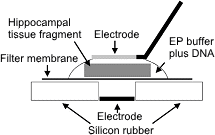
Schematic representation of an electroporation set-up.
A fragment of the mouse embryonic hippocampus was placed on a Millipore membrane filter and 5μl EP buffer containing 1mg/ml of plasmid DNA was applied onto the tissue.
A tungsten needle was attached to the surface of a droplet.
After application of square pulses the tissue fragment was returned to a petri dish containing ice-cold HBSS solution.
Electroporation-mediated expression of fluorescent proteins in hippocampal neurons.
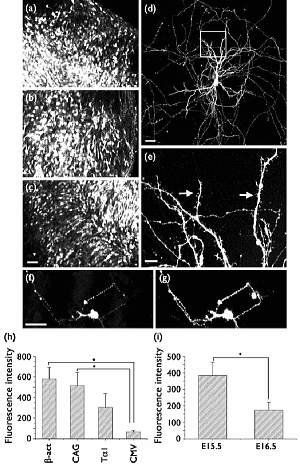
(a-c) Organ culture of hippocampal tissue fragments three days after electroporation with CAG-eGFP
(a) Ta1X4 -eGFP, (b) and b-actin-eGFP, (c) expression constructs.
(d,e) A mature hippocampal neuron maintained 14 days in dissociated culture after electroporation of a -actin-eGFP expression construct. Higher magnification view of the region marked by a rectangle in (d) reveals dendritic spines on the surface of dendritic shafts (arrows in e).
(f,g) A hippocampal neuron 7 days after electroporation of 1:1 mixture of Ta1X4-eGFP and Ta1X4-mRFP1. Both eGFP fluorescence (f) and mRFP1 fluorescence (g) can be observed in a single cell.
(h) Relative fluorescence intensity of hippocampal tissue fragments after electroporation of eGFP-expression plasmids with four different promoter sequences. The tissue fragments were maintained in culture for 4 days, fixed and observed under a confocal microscope. Fluorescence intensities per unit area of the tissue fragments were determined.
(i) 2Relative fluorescence intensity of hippocampal tissue fragments isolated at two different developmental stages and electroporated with b-actin-eGFP. Tissue fragments were maintained for 4 days in culture and subsequently fixed. Fluorescence intensities were measured using a confocal microscope.
Shigeo Okabe, Department of Cellular Neurobiology, Graduate School of Medicine and Faculty of Medicine, The University of Tokyo
*Neuroreport, Volume 15, Issue 6, Pages 971-975, April 29, 2004
PUBLICATIONS
- Cerebellum_lobe_culture
- P5_mice
Nesprin-2 coordinates opposing microtubule motors during nuclear migration in neurons
Zhou, C., Wu, Y. K., Ishidate, F., Fujiwara, T. K., Kengaku, M.
J Cell Biol. 2024 Nov 4;223(11):e202405032.
- P2_mouse_brains
- P21_mouse_brains
Primary cilium-dependent cAMP/PKA signaling at the centrosome regulates neuronal migration
Stoufflet J, Chaulet M, Doulazmi M, Fouquet C, Dubacq C, Métin C, Schneider-Maunoury S, Trembleau A, Vincent P, Caillé I.
Sci Adv. 2020 Sep 2;6(36):eaba3992.
- Cortical_slices
- P0_hamster_brains
Cortical excitatory neurons become protected from cell division during neurogenesis in an Rb family-dependent manner.
Oshikawa M, Okada K, Nakajima K, Ajioka I.
Development. 2013 Jun;140(11):2310-20.
- New_born_mouse_brains
Cellular Mechanismhs Underlying Morphine Analgesic Tolerance and Hyperalgesia
Hiroshi Ueda
Opioid-Induced Hyperalgesia, First, Pages 9-20, October 2009
- P0_P4_mouse_brains
Efficient In Vivo Electroporation of the Postnatal Rodent Forebrain
Boutin C, Diestel S, Desoeuvre A, Tiveron MC, Cremer H.
PLoS One. 2008 Apr 2;3(4):e1883.
Electroporation
■ Cell Cultures
- Primary Cell Cultures
- Stem Cells
- Organoids
- Cell Lines
- Cells in Adherence
■ In Vivo Mice/Rats
- Zygotes In Vitro (TAKE method)
- Zygotes In Oviduct (i-GONAD method)
- Embryos In Utero
- Ex Utero Embryos In Vitro
- Brain
- Retina / Cornea / Spinal Cord / Sciatic Nerve
- Lung / Spleen / Liver / Stomach/ Kidney / Intestine
- Pancreas / Islets of langerhans
- Testis / Ovary / Prostate / Gonad / Uterus
- Muscle / Skin / Joint / Cartilage / Tumor / Others
■ In Vivo Other Animals
- Bovine/Porcine/Other Animal Zygotes
- Hamster Zygotes in Oviduct (i-GONAD method)
- Monkey Skin
- Chicken (In Ovo・Others)
- Zebrafish & Other Fishes
- Insects・Others
■ Plant Cells & Algae
- Plant Cells
- Algae
■ Exosomes
- Exosomes
■ Bacteria, Yeast, Fungi
- E. coli/Bacterial Cells
- Yeasts/Fungi
- Bacterial cells/Yeasts/Fungi (NEPA Porator)
Drug Delivery and Transfection
■ Ultrasound Transfection and Drug Delivery (Sonoporation/Fus)
- Brain
- Liver/Skin/Other Applications
- Heart
- Cell Culture
- Lung
- Muscle
Electro Cell Fusion
■ Hybridoma Production
- Monoclonal antibodies, etc
■ Oocyte Activation
- Electrical stimulation before/after Intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI)
■ Somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT)・ Oocytes Nuclear Transfer
- Animal cloning
■ Tetraploid Embryos Production
- 2 Cell Embryos (Tetraploid)
■ Other Applications
- Liposome・Protoplast・Yeast, etc.
Fluorescence Quenching / in situ Hybridization Chain Reaction
■ Autofluorescence Quenching
- Mammalian Tissue Sections
- Fish Tissue Sections
- Amphibia Tissue Sections
- Avian Tissue Sections
- Plant Tissue Sections
- Chordate Tissue Sections
■ in situ HCR
- Detection of Target mRNA
Single-Cell/Micro-Particle Transfer
■ Micro targets
- Animal cells
■ Micro liquid
- Plant cells
Cell Freezing
■ Cell Therapy
- Stem cells, primary cells, and more
■ Animal Husbandry
- Sperm, embryos, tissues, and more