Transfection into Mouse/Rat Cultured Embryos by Ex Utero Electroporation
APPLICATIONS
Electroporation for mammalian embryos in the whole embryo culture system
Procedures
- ProcedureProcedure1: Pre-culture embryos in the whole embryo culture system for 1.5-2 hours prior to electroporation.
- Place the embryo in a Petri dish with Tyrode’s solution.
- Inject 0.1-0.5 μl of plasmid DNA into the brain ventricle with a fine capillary.
- Apply square pulses using the electroporator (CUY21) and electrodes (chamber-type and forceps-type electrodes are available). 70V, 50 msec at 1-second interval, five pulses are applied for E10.5 mouse embryos.
- Culture the electroporated embryos for 24-48 hours in the whole embryo culture system.Transfection of a fluorescent protein-expression vector into the developing rat cortex.
Transfection of a fluorescent protein-expression vector into the developing rat cortex.
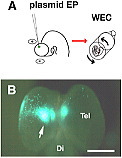
(A) EGFP-expression vector was electroporated into E11.5 rat telencephalon. The electroporated embryo was cultured in the whole embryo culture system (WEC).
(B) 24 hours after electroporation, EGFP-expression was specifically detected at the dorsal part of the telencephalon.
Tel: telencephalon;
Di: diencephalon
Transfection of fluorescent protein-expression vectors into the rat spinal cord.
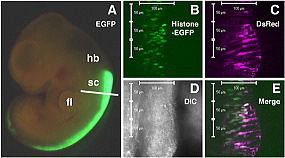
(A) EGFP-expression vector was transfected into the spinal cord of E12.5 rat embryos by electroporation. The electroporated embryos were cultured for 24 hours in the whole embryo culture system (WEC).
(B-E) Time-lapse analysis of neuroepithelial cells in the slice culture system. Histon-EGFP- and DsRed2-expression vectors were co-electroporated into the E12.0 rat spinal cord. The electroporated embryo was cultured for 24 hours in the WEC, then the spinal cord was sliced and time-lapse recording was performed.
(B-E) Cell nuclei (B, green) and cytoplasms (C, magenta) of neuroepithelial cells in the slice are simultaneously labeled by the electroporation
(E). (D) A DIC image.
hb: hindbrain; sc: spinal cord; fl: forelimb; DIC: differential interference contrast.
Masanori Takahashi, Tadashi Nomura, Noriko Osumi, Department of Developmental Neurobiology, Tohoku University Graduate School of Medicine
*Differentiation, Volume 70, Issue 4-5, Pages 155-162, June 2002
PUBLICATIONS
Electroporation
■ Cell Cultures
- Primary Cell Cultures
- Stem Cells
- Organoids
- Cell Lines
- Cells in Adherence
■ In Vivo Mice/Rats
- Zygotes In Vitro (TAKE method)
- Zygotes In Oviduct (i-GONAD method)
- Embryos In Utero
- Ex Utero Embryos In Vitro
- Brain
- Retina / Cornea / Spinal Cord / Sciatic Nerve
- Lung / Spleen / Liver / Stomach/ Kidney / Intestine
- Pancreas / Islets of langerhans
- Testis / Ovary / Prostate / Gonad / Uterus
- Muscle / Skin / Joint / Cartilage / Tumor / Others
■ In Vivo Other Animals
- Bovine/Porcine/Other Animal Zygotes
- Hamster Zygotes in Oviduct (i-GONAD method)
- Monkey Skin
- Chicken (In Ovo・Others)
- Zebrafish & Other Fishes
- Insects・Others
■ Plant Cells & Algae
- Plant Cells
- Algae
■ Exosomes
- Exosomes
■ Bacteria, Yeast, Fungi
- E. coli/Bacterial Cells
- Yeasts/Fungi
- Bacterial cells/Yeasts/Fungi (NEPA Porator)
Drug Delivery and Transfection
■ Ultrasound Transfection and Drug Delivery (Sonoporation/Fus)
- Brain
- Liver/Skin/Other Applications
- Heart
- Cell Culture
- Lung
- Muscle
Electro Cell Fusion
■ Hybridoma Production
- Monoclonal antibodies, etc
■ Oocyte Activation
- Electrical stimulation before/after Intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI)
■ Somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT)・ Oocytes Nuclear Transfer
- Animal cloning
■ Tetraploid Embryos Production
- 2 Cell Embryos (Tetraploid)
■ Other Applications
- Liposome・Protoplast・Yeast, etc.
Fluorescent Staining
■ Autofluorescence Quenching
- Mammalian Tissue Sections
- Fish Tissue Sections
- Amphibia Tissue Sections
- Avian Tissue Sections
- Plant Tissue Sections
- Chordate Tissue Sections
■ in situ Hybridization Chain Reaction (HCR)
- Fluorescence Detection of Target mRNA
Single-Cell/Micro-Particle Transfer
■ Micro targets
- Animal cells
■ Micro liquid
- Plant cells
Cell Freezing
■ Cell Therapy
- Stem cells, primary cells, and more
■ Animal Husbandry
- Sperm, embryos, tissues, and more